Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
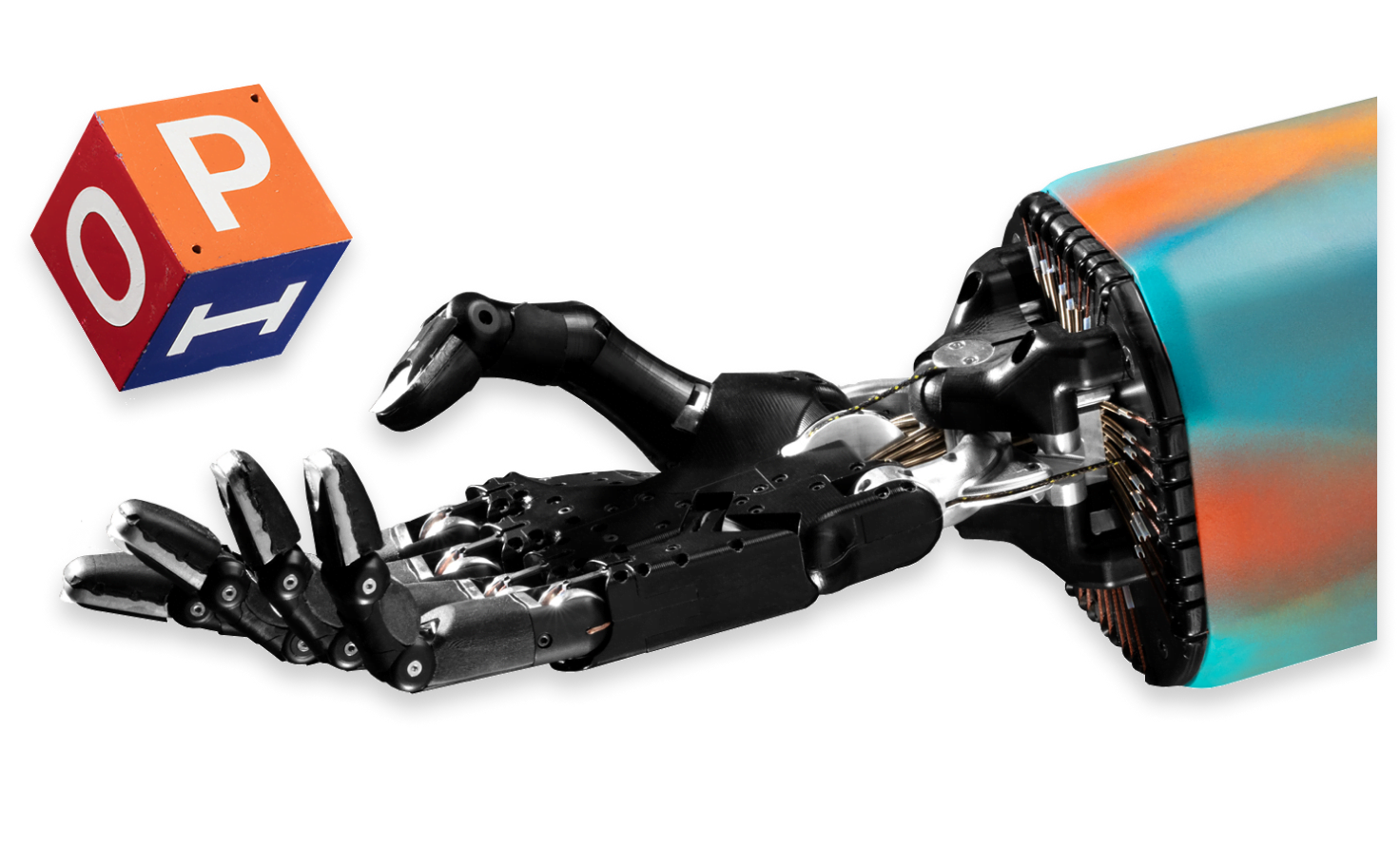


You can train our Shadow Dexterous Hand to manipulate physical objects and complete goal-orientated tasks intuitively.
Researchers have used neural networks to train our robot Hand in simulation using the trial-and-error principle (reinforcement learning).
The data is then transferred to our robot Hand so that it can perform the desired action in a real-life setting and in real-time.
The Dextrous Hands have over 100 sensors running at up to 1KHz, giving you insight and accurate data points supporting your research.
Our robots are an incredible source of data with our Hand being an unrivalled system available to researchers around the globe.
Our systems run on ROS, so you can use data immediately in ROS nodes or record to ROSbags for later analysis and learning.
The data collected has a wide variety of ways you can use them:
It can be used in Deep Learning where one uses machine learning to create dynamics models to develop new control methods and to verify the quality of simulations.
Imitation learning - using the data from the teleoperation system to help teach learning systems how to perform task.
Reinforcement learning - using the data to learn how to interact with environments or manipulate objects.

Abduct/Adduct
Each finger has an independent side-to-side motion for impressive in-hand manipulation and other movements with advanced dexterity
“They who have the most data win” - This is why Shadow Dexterous Hands include a variety of sensors that provide you with precise data at a rate of up to 1kHz.The hand includes 20 motors, each equipped with temperature, voltage and current sensors, and left and right strain gauges.
There are two tendons on each joint going to the motors - the load on each tendon is measured by the respective strain gauge.
We’ve worked with OpenAI, founded by business tycoons, Elon Musk and Sam Altman to advance research within AI and machine learning using the Shadow Dexterous Hand.

HBP and Maastricht University successfully integrate and simulate the Shadow Hand on the HBP Neurorobotics Platform which connects a physics simulator to a variety of neural networks (or brains).

Google Brain used the Shadow Hand to learn how to manipulate multiple objects using just a few hours of real-world data.
Don’t miss out on the opportunity to be among the first to access our exclusive pre-release white paper on the use of Dexterous Hands in AI and Machine Learning. Sign up now to be the first to receive a copy of the white paper as soon as it becomes available.
Don’t wait, sign up now and stay ahead of the curve in the world of AI and machine learning.

Shadow is a proud winner of Awards.
AI 2020 and the AIconics Award 2019 for Best Innovation in AI Hardware

We’ve worked with OpenAI, founded by business tycoons, Elon Musk and Sam Altman to advance research within AI and machine learning using the Shadow Dexterous Hand.
OpenAI used the Shadow Hand to study ways of learning dexterity using the complex task of solving a Rubik’s cube single-handedly.
They trained their system entirely in simulation via reinforcement learning.
Shadow Dexterous Hand demonstrated the learnings in the real world. No fine-tuning needed.
Featured on BBC News and the front page of the New York Times.

HBP and Maastricht University successfully integrate and simulate the Shadow Hand on the HBP Neurorobotics Platform which connects a physics simulator to a variety of neural networks (or brains).
The Human Brain Project added the virtual Shadow Hand to their EBRAINS infrastructure to learn more about how the brain coordinates complex hand movements.
Each Shadow Hand joint can be individually linked to both the input and/or output of the brain.
Contact-based feedback is forwarded to the brain. No need for time-consuming physical setups.

Google Brain used the Shadow Hand to learn how to manipulate multiple objects using just a few hours of real-world data.
The team used a novel robot task planning technique involving deep dynamics models (DDM).
They were able to manipulate multiple objects with just four hours of real-world data.
Read more about Google Brain's results with Shadow Hand manipulation.

“People are able to perform a wide range of dexterous manipulation tasks in a diverse set of environments, making the human hand a grounded source of inspiration for research into robotic manipulation”
OpenAI

“The Shadow Hand exhibits human-level dexterity which allows a research team at Maastricht University to study how the brain coordinates complex hand movements… By providing a highly realistic model of the human hand, the Shadow Hand allows neuroscientists to develop more realistic models around how the human brain works.”
Mario Senden, Assistant Professor
Faculty of Psychology and Neuroscience at Maastricht University
Learn more about our product's capabilities for Deep Learning.